|
|
| |
|

|
|
|
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Gate and Switch delays
|
|
|
In real circuits, logic gates have delays associated with them. Verilog provides the mechanism to associate delays with gates. |
| |
|

|
|
|
- Rise, Fall and Turn-off delays.
- Minimal, Typical, and Maximum delays.
|
| |
|

|
|
|
In Verilog delays can be introduced with #'num' as in the examples below, where # is a special character to introduce delay, and 'num' is the number of ticks simulator should delay current statement execution. |
| |
|

|
|
|
- #1 a = b : Delay by 1, i.e. execute after 1 tick
- #2 not (a,b) : Delay by 2 all assignments made to a.
|
| |
|

|
|
|
Real transistors have resolution delays between the input and output. This is modeled in Verilog by specifying one or more delays for the rise, fall, turn-on and turn off time seperated by commas. |
| |
|

|
|
|
Syntax: keyword #(delay{s}) unique_name (node specifications); |
| |
|

|
|
|
|
Switch element
|
Number Of Delays
|
Specified delays
|
|
Switch
|
1
|
Rise, fall and turn-off times of equal length
|
|
|
2
|
Rise and fall times
|
|
|
3
|
Rise, fall and turn off
|
|
(r)tranif0, (r)tranif1
|
1
|
both turn on and turn off
|
|
|
2
|
turn on, turn off
|
|
(r)tran
|
0
|
None allowed
|
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
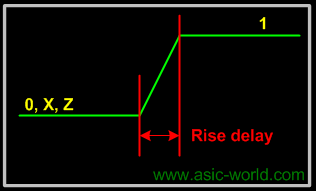
Rise Delay
|
|
|
The rise delay is associated with a gate output transition to 1 from another value (0, x, z). |
| |
|

|
|
|
 |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
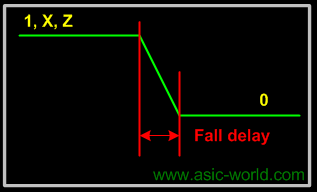
Fall Delay
|
|
|
The fall delay is associated with a gate output transition to 0 from another value (1, x, z). |
| |
|

|
|
|
 |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Turn-off Delay
|
|
|
The Turn-off delay is associated with a gate output transition to z from another value (0, 1, x). |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Min Value
|
|
|
The min value is the minimum delay value that the gate is expected to have. |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Typ Value
|
|
|
The typ value is the typical delay value that the gate is expected to have. |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Max Value
|
|
|
The max value is the maximum delay value that the gate is expected to have. |
| |
|

|
|
|
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Example
|
|
|
Below are some examples to show the usage of delays. |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
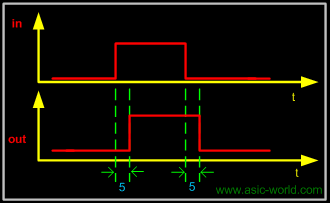
Example - Single Delay
|
| |
|

|
|
|
1 module buf_gate ();
2 reg in;
3 wire out;
4
5 buf #(5) (out,in);
6
7 initial begin
8 $monitor ("Time = %g in = %b out=%b", $time, in, out);
9 in = 0;
10 #10 in = 1;
11 #10 in = 0;
12 #10 $finish;
13 end
14
15 endmodule
You could download file buf_gate.v here
|
| |
|

|
|
|
Time = 0 in = 0 out=x
Time = 5 in = 0 out=0
Time = 10 in = 1 out=0
Time = 15 in = 1 out=1
Time = 20 in = 0 out=1
Time = 25 in = 0 out=0
|
| |
|

|
|
|
 |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
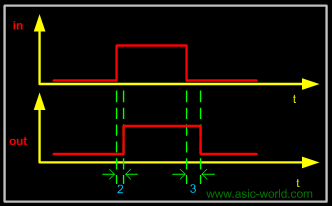
Example - Two Delays
|
| |
|

|
|
|
1 module buf_gate1 ();
2 reg in;
3 wire out;
4
5 buf #(2,3) (out,in);
6
7 initial begin
8 $monitor ("Time = %g in = %b out=%b", $time, in, out);
9 in = 0;
10 #10 in = 1;
11 #10 in = 0;
12 #10 $finish;
13 end
14
15 endmodule
You could download file buf_gate1.v here
|
| |
|

|
|
|
Time = 0 in = 0 out=x
Time = 3 in = 0 out=0
Time = 10 in = 1 out=0
Time = 12 in = 1 out=1
Time = 20 in = 0 out=1
Time = 23 in = 0 out=0
|
| |
|

|
|
|
 |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Example - All Delays
|
| |
|

|
|
|
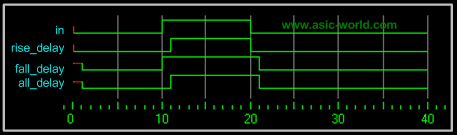
1 module delay();
2 reg in;
3 wire rise_delay, fall_delay, all_delay;
4
5 initial begin
6 $monitor (
7 "Time=%g in=%b rise_delay=%b fall_delay=%b all_delay=%b",
8 $time, in, rise_delay, fall_delay, all_delay);
9 in = 0;
10 #10 in = 1;
11 #10 in = 0;
12 #20 $finish;
13 end
14
15 buf #(1,0)U_rise (rise_delay,in);
16 buf #(0,1)U_fall (fall_delay,in);
17 buf #1 U_all (all_delay,in);
18
19 endmodule
You could download file delay.v here
|
| |
|

|
|
|
Time = 0 in = 0 rise_delay = 0 fall_delay = x all_delay = x
Time = 1 in = 0 rise_delay = 0 fall_delay = 0 all_delay = 0
Time = 10 in = 1 rise_delay = 0 fall_delay = 1 all_delay = 0
Time = 11 in = 1 rise_delay = 1 fall_delay = 1 all_delay = 1
Time = 20 in = 0 rise_delay = 0 fall_delay = 1 all_delay = 1
Time = 21 in = 0 rise_delay = 0 fall_delay = 0 all_delay = 0
|
| |
|

|
|
|
 |
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Example - Complex Example
|
| |
|

|
|
|
1 module delay_example();
2
3 wire out1,out2,out3,out4,out5,out6;
4 reg b,c;
5
6 // Delay for all transitions
7 or #5 u_or (out1,b,c);
8 // Rise and fall delay
9 and #(1,2) u_and (out2,b,c);
10 // Rise, fall and turn off delay
11 nor #(1,2,3) u_nor (out3,b,c);
12 //One Delay, min, typ and max
13 nand #(1:2:3) u_nand (out4,b,c);
14 //Two delays, min,typ and max
15 buf #(1:4:8,4:5:6) u_buf (out5,b);
16 //Three delays, min, typ, and max
17 notif1 #(1:2:3,4:5:6,7:8:9) u_notif1 (out6,b,c);
18
19 //Testbench code
20 initial begin
21 $monitor (
22 "Time=%g b=%b c=%b out1=%b out2=%b out3=%b out4=%b out5=%b out6=%b",
23 $time, b, c , out1, out2, out3, out4, out5, out6);
24 b = 0;
25 c = 0;
26 #10 b = 1;
27 #10 c = 1;
28 #10 b = 0;
29 #10 $finish;
30 end
31
32 endmodule
You could download file delay_example.v here
|
| |
|

|
|
|
Time = 0 b = 0 c=0 out1=x out2=x out3=x out4=x out5=x out6=x
Time = 1 b = 0 c=0 out1=x out2=x out3=1 out4=x out5=x out6=x
Time = 2 b = 0 c=0 out1=x out2=0 out3=1 out4=1 out5=x out6=z
Time = 5 b = 0 c=0 out1=0 out2=0 out3=1 out4=1 out5=0 out6=z
Time = 8 b = 0 c=0 out1=0 out2=0 out3=1 out4=1 out5=0 out6=z
Time = 10 b = 1 c=0 out1=0 out2=0 out3=1 out4=1 out5=0 out6=z
Time = 12 b = 1 c=0 out1=0 out2=0 out3=0 out4=1 out5=0 out6=z
Time = 14 b = 1 c=0 out1=0 out2=0 out3=0 out4=1 out5=1 out6=z
Time = 15 b = 1 c=0 out1=1 out2=0 out3=0 out4=1 out5=1 out6=z
Time = 20 b = 1 c=1 out1=1 out2=0 out3=0 out4=1 out5=1 out6=z
Time = 21 b = 1 c=1 out1=1 out2=1 out3=0 out4=1 out5=1 out6=z
Time = 22 b = 1 c=1 out1=1 out2=1 out3=0 out4=0 out5=1 out6=z
Time = 25 b = 1 c=1 out1=1 out2=1 out3=0 out4=0 out5=1 out6=0
Time = 30 b = 0 c=1 out1=1 out2=1 out3=0 out4=0 out5=1 out6=0
Time = 32 b = 0 c=1 out1=1 out2=0 out3=0 out4=1 out5=1 out6=1
Time = 35 b = 0 c=1 out1=1 out2=0 out3=0 out4=1 out5=0 out6=1
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
N-Input Primitives
|
|
|
The and, nand, or, nor, xor, and xnor primitives have one output and any number of inputs |
| |
|

|
|
|
- The single output is the first terminal.
- All other terminals are inputs.
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Examples
|
| |
|

|
|
|
1 module n_in_primitive();
2
3 wire out1,out2,out3;
4 reg in1,in2,in3,in4;
5
6 // Two input AND gate
7 and u_and1 (out1, in1, in2);
8 // four input AND gate
9 and u_and2 (out2, in1, in2, in3, in4);
10 // three input XNOR gate
11 xnor u_xnor1 (out3, in1, in2, in3);
12
13 //Testbench Code
14 initial begin
15 $monitor (
16 "in1 = %b in2 = %b in3 = %b in4 = %b out1 = %b out2 = %b out3 = %b",
17 in1, in2, in3, in4, out1, out2, out3);
18 in1 = 0;
19 in2 = 0;
20 in3 = 0;
21 in4 = 0;
22 #1 in1 = 1;
23 #1 in2 = 1;
24 #1 in3 = 1;
25 #1 in4 = 1;
26 #1 $finish;
27 end
28
29 endmodule
You could download file n_in_primitive.v here
|
| |
|

|
|
|
in1 = 0 in2 = 0 in3 = 0 in4 = 0 out1 = 0 out2 = 0 out3 = 1
in1 = 1 in2 = 0 in3 = 0 in4 = 0 out1 = 0 out2 = 0 out3 = 0
in1 = 1 in2 = 1 in3 = 0 in4 = 0 out1 = 1 out2 = 0 out3 = 1
in1 = 1 in2 = 1 in3 = 1 in4 = 0 out1 = 1 out2 = 0 out3 = 0
in1 = 1 in2 = 1 in3 = 1 in4 = 1 out1 = 1 out2 = 1 out3 = 0
|
| |
|

|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
N-Output Primitives
|
|
|
The buf and not primitives have any number of outputs and one input |
| |
|

|
|
|
- The outputs are the first terminals listed.
- The last terminal is the single input.
|
| |
|

|
| |
 |
Examples
|
| |
|

|
|
|
1 module n_out_primitive();
2
3 wire out,out_0,out_1,out_2,out_3,out_a,out_b,out_c;
4 wire in;
5
6 // one output Buffer gate
7 buf u_buf0 (out,in);
8 // four output Buffer gate
9 buf u_buf1 (out_0, out_1, out_2, out_3, in);
10 // three output Invertor gate
11 not u_not0 (out_a, out_b, out_c, in);
12
13 endmodule
You could download file n_out_primitive.v here
|
| |
|

|
| |
|

|
| |
|

|
|
|
|
| |
|

|
|
|